If our bodies performed exactly as they were designed to there would be no need for corrective exercise. Whether walking down the street, picking up a child, hitting a tennis ball or performing a squat in the gym, our body’s movements should happen because a group of muscles works in harmony, each with their specific role to play.
The muscle teamwork
Hip extension, a movement we perform thousands of times a day, happens when we stand up from sitting, when we walk, run or climb up stairs, when we come out of a squat or lunge… and is a great example to work with.
The prime mover or “agonist” muscle takes the lead role in a movement. In hip extension the agonist is our gluteus maximus – our butt muscles or glute max! Think rising up out of a squat… as our glute max contracts, the angle of our hip joint opens and our body moves into a standing posture.
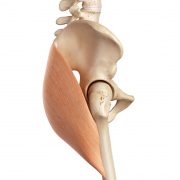
Gluteus maximus
“Synergist” muscles provide assistance to the prime mover. Our erector spinae (group of muscles running the length of the spine) and our hamstring complex (group of muscles at the back of the thighs) are synergists to our glute max in hip extension.
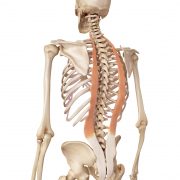
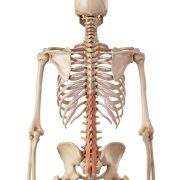
Erector spinae – iliocostalis
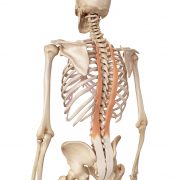
Erector spinae – longissimus
“Stabiliser” muscles support the body while the movement is taking place, maintaining proper joint alignment and minimising the risk of injury. In hip extension the stabilisers are our core muscles: transversus abdominis, internal obliques, multifidus, and deep erector spinae muscles.
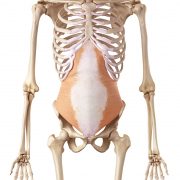
Transversus abdominis
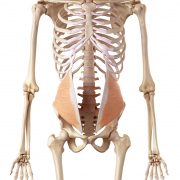
Internal obliques
Multifidus
Lastly, the “antagonist” muscle acts in direct opposition to the agonist and should remain relaxed, allowing the movement to happen safely. Our psoas muscle (hip flexor) is antagonist to our glute max.
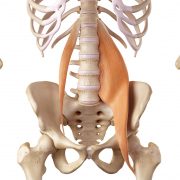
Psoas minor and major muscles
How might this carefully balanced muscular cooperation break down and what would be the implications?
Movement impairment
Injury (recent or not), repetitive movement or repetitive lack of movement can lead to “faulty” movement patterns. This means that although movement happens it doesn’t happen optimally with the appropriate muscles taking on the various roles. These faulty movement patterns are often accompanied by tension and pain.
Consider how much time some people spend in a seated position: at their desk, in front of a computer, behind a counter, in the car, watching TV. If you’re sitting down as you read this, first sit up straight and then place your hand in the 90° angle between your thigh and your torso.
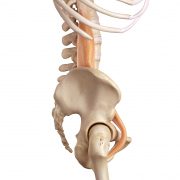
Psoas major
Your hip flexor is running across that angle and as long as you remain seated the muscle is contracting, working to hold your body upright. In this position it has no opportunity to lengthen and stretch. While your hip flexors are at work, your glutes are relaxed and stretched across your butt (agonist-antagonist). With habitual sitting the glutes become over-extended and underactive, rather like an over-stretched elastic band.
Let’s now observe the chain reaction that might unfold over time…
Imagine you’ve been sitting at a desk for an extended period and now you stand up… yes, up you get! Your body suddenly wants that 90° angle to become 180°. If your hip flexors are tight from overuse that’s not necessarily going to be easy.
Your glutes have been rudely awakened from a pretty relaxing day, while your hip flexors are finding it difficult to switch off. Your hip joints only extend to say 170°, so your torso is pulled forward into a slight bow.
Without changing the angle at your hip joints – precisely because we’re imagining your hip flexors to be too tight to allow this – try to move your upper body into an upright position, one in which your chest is lifted and your eyes are looking directly ahead. To do this you’ll need to arch your lower back.
What’s happening here? Since your glute max are unable to outdo their overactive and shortened antagonist hip flexors, other muscles are taking over. Your erector spinae, the muscles responsible for extension of the spine, shift from their synergistic role to a more dominant role, creating the arch in your back that brings you to a more upright position.
If over time this pattern of restricted movement at the hip joints persists, some of your core stabilising muscles will become underactive, adding even more workload to the muscles of your back. A likely outcome of this chain reaction is the all too frequently experienced lower back pain.
The four steps of corrective exercise
A lot of the time it won’t be possible to drastically change the behaviour that is causing the faulty movement pattern. The good news is corrective exercise can mitigate its impact and return the body to optimal performance and free from pain.
Step 1: Inhibition
The first step is to reverse the condition that started the chain reaction; inhibiting the overactive muscle that brought about the faulty movement pattern. In our example this is the hip flexor. In the training environment this is typically achieved using foam rolling, technically referred to as self-myofascial release (SMR). Other therapeutic input such as physiotherapy or biokinetics may also be beneficial.
Step 2: Lengthening
With tension released and over-activity reduced (inhibition) the same muscle can now be lengthened, creating space for other muscles in the body to perform more effectively. An increase in extensibility and range of motion in the hip flexor will allow the gluteus maximus to contract more readily and completely. Static and dynamic stretching of the hip flexor will achieve this.
Step 3: Activation
Now that it’s able to move more freely, the currently underactive agonist muscle (in our example the glute max) can be re-educated and strengthened using simple exercises that isolate the muscle as much as possible. Glute activation can be achieved using simple squat movements such as suspension squats (TRX) and stability-ball wall squats.
Step 4: Integration
The final step is to retrain the muscles as a team using progressively more complex exercises that require each team member to perform their correct role as agonist, synergist, stabiliser or antagonist. These would be functional exercises that mimic the movement patterns that have until now be compromised. Think squats and lunges and gradually add the challenge of stability (BOSU), balance (single-leg work), integration (adding upper body movements) and power (performing jumps and turns).
Identifying a need for corrective exercise
As a personal trainer with a corrective exercise specialisation I use several tools to identify faulty movement patterns in my clients, the simplest one being targeted questioning. Understanding my client’s job and the physical demands it places on them, knowing the sporting activities he or she takes part in and the hobbies they enjoy, being aware of past injuries or surgeries, piecing together a picture of their life… this information will tell me a lot about how my client moves and where stresses might regularly be placed on their body. In a training session I’ll call on static postural and dynamic movement assessments to highlight where movement compensations are being made and tension is being placed.
The next step is to design a bespoke corrective exercise programme for my client. Applying the four steps is a gradual process which, if done properly, will bring their body to a state of balance and optimal performance.
Deborah Savin-Curnier















 I decided the best approach would be to run the course at least once a week and I stuck to this plan, always managing to pick the perfect weather conditions and calling on my mantra to get me up onto the trail – the stunning views my reward for getting to the top.
I decided the best approach would be to run the course at least once a week and I stuck to this plan, always managing to pick the perfect weather conditions and calling on my mantra to get me up onto the trail – the stunning views my reward for getting to the top.